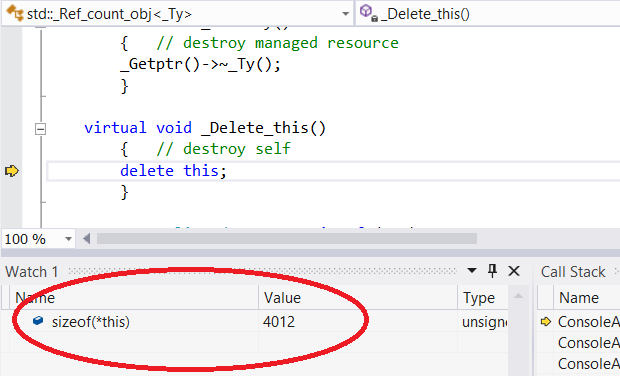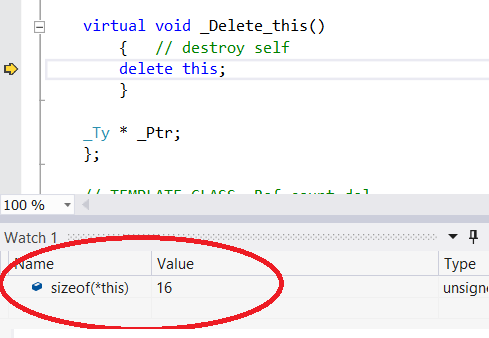
Using new, counters are allocated separatelly, them the object and memory is dealocated with de last shared_ptr remaning only weakpointer counters.
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
struct X
{
int b[1000];
};
int main()
{
{
weak_ptr<X> wp; //lives longer than shared_ptr
{
shared_ptr<X> sp(new X());
wp = sp;
}
}
}

makeshared makes a single alloc with the object plus counters. The object destructor is called with the last sharedptr, however the memory used by the object is dealocated only with the last weak_ptr.
From the standard:
Remarks: Implementations are encouraged, but not required, to perform no more than one memory
allocation. Note: this provides efficiency equivalent to an intrusive smart pointer. end note
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
struct X
{
int b[1000];
};
int main()
{
{
weak_ptr<X> wp; //lives longer than shared_ptr
{
shared_ptr<X> sp = make_shared<X>();
wp = sp;
}
}
}